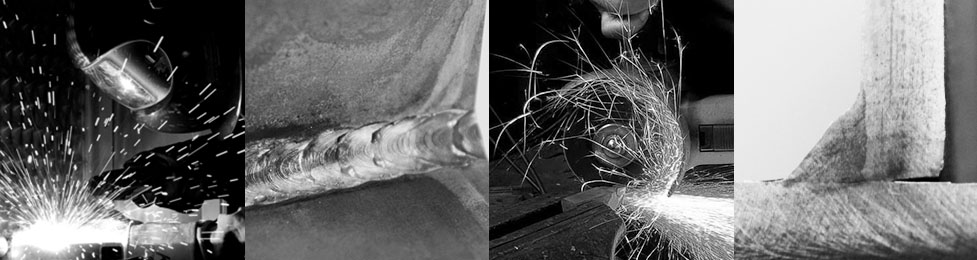
Metal fabrication is the process of making metallic products from raw materials, metal sheets, or extrusions. Metal fabricators employ various manufacturing techniques to design, cut, form and assemble metallic components.
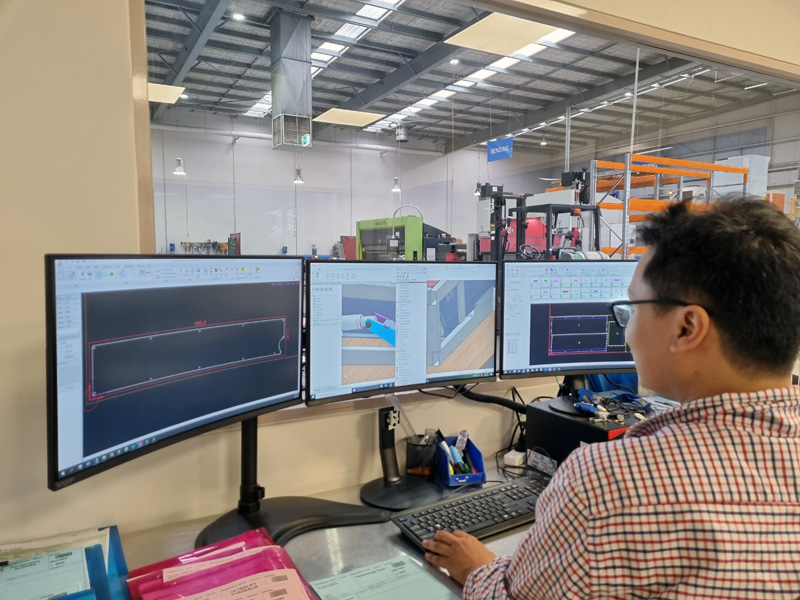
New technologies like Computer-Aided Design (CAD), laser cutting, and CNC folding have made the manufacturing process more accurate. These new advances have also reduced turnaround times. The modern metal fabrication processes include CAD, cutting, machining, bending, welding, and assembling.
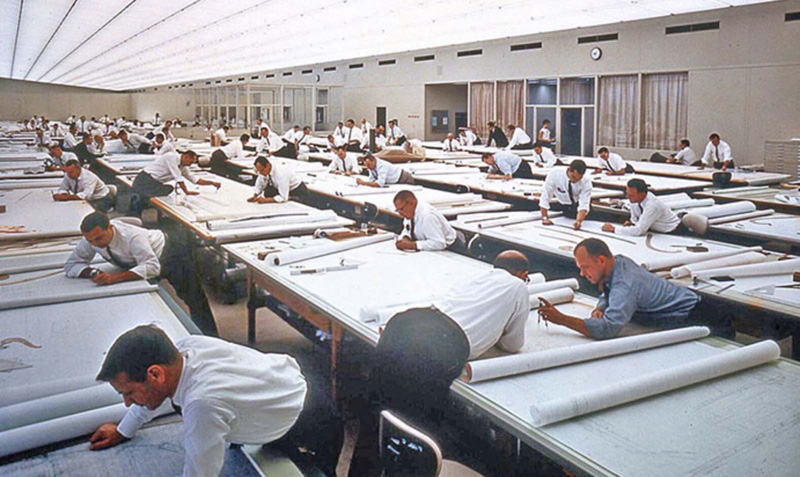


Modern technologies have improved the metal fabrication industry and the way engineers design and manufacture products. Left: General Motors Technical Center in Warren Michigan, the 1950s. Right: CAD software used by our metal fabrication engineers to design parts and assemblies.
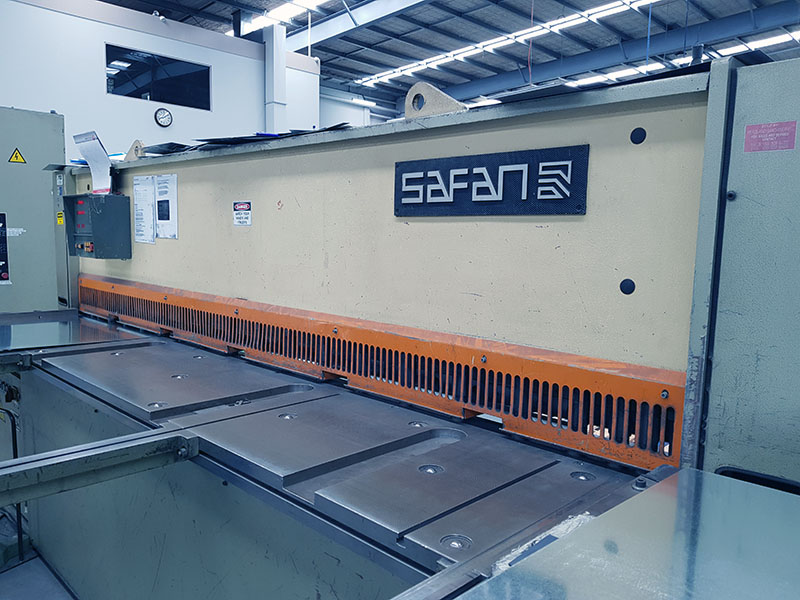
At Westberg, we use a flatbed laser cutter to cut steel and aluminium sheet metal. Our metal fabrication in Melbourne includes a rotary tube laser cutter as well. The tube laser cutter can cut sophisticated patterns and holes on metal extrusions and tubes. Guillotine cutters are also used for simple cuts or materials that should not be exposed to the laser’s higher temperatures.


Laser cutters use high-power laser beams to melt the metal. High-pressure gas (nitrogen, air, or carbon dioxide) is used to blow the molten metal out and finish the cut.
After cutting, any hole or pattern that cannot be made using the laser cutters is made in the machining stage. The required holes, threads, and slots can be made using various machining equipment including lathe, CNC milling, and drilling. Following the machining process, CNC press brakes are used to bend and form the product.
The metallic parts are then put and secured together by welding or using rivets and screws. Any final finish and painting (e.g. powder coating) can be used before or after the assembly to finalise the metal fabrication process.
How to learn metal fabrication:
High-quality metal fabrication does not rely only on the quality of the machines and processes. Having an experienced team is the most important factor to guarantee the highest quality of the provided metal fabrication services.
Metal fabrication experts learn the required skills by attending TAFE and technical schools in Australia. The programs include a mix of theoretical and practical courses. Students work as apprentices as part of their TAFE program and under the supervision of experienced metal fabricators.
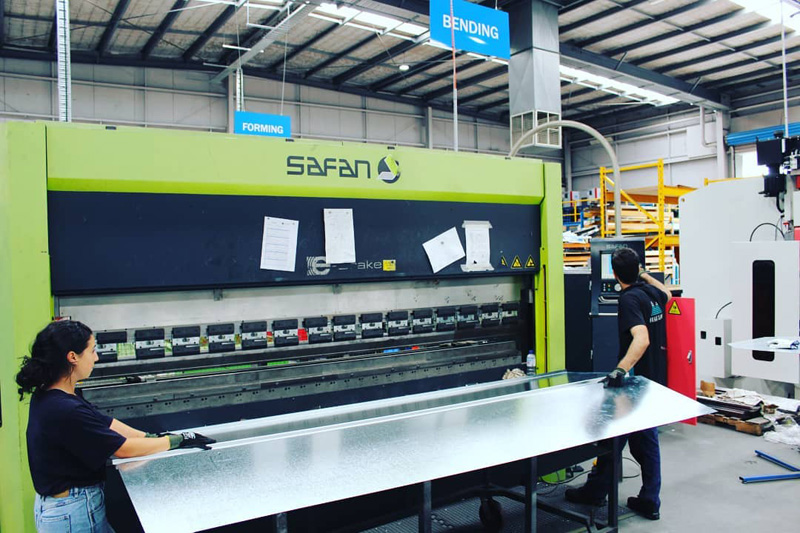

Apprentices learn various metal fabrication skills by working under the supervision of skilled workers as part of their program at TAFE.
We have custom metal fabrication apprentices as part of our team in Melbourne. If you like to join our team, send us an email with your resume or give us a call.
We have a dedicated metal fabrication team at Westberg Sheet Metal. You can also join the production team of Ultralift Australia. Ultralift provides custom steel and aluminium products for the AV industry.